Digital computers have become an integral part of modern life, transforming how we work, learn, and entertain ourselves. At their core, digital computers process information using numbers, primarily 0s and 1s. They receive input, process it through a central system, and produce output quickly and accurately. From browsing the internet to playing games, digital computers make tasks faster, easier, and more efficient.
Read More: Revolutionary Hybrid Computers: Unleashing Unmatched Speed and Innovation
A Brief History of Digital Computers
The journey of digital computers began decades ago, driven by the need to solve problems faster and more efficiently. The first significant breakthrough occurred in 1946 with the creation of ENIAC (Electronic Numerical Integrator and Computer). Built by John Mauchly and J. Presper Eckert, ENIAC was designed to perform complex mathematical calculations at unprecedented speeds. Unlike its analog predecessors, which relied on signals and mechanical parts, ENIAC used digital technology, processing data as numbers—zeros and ones.
ENIAC was enormous, occupying an entire room, but it marked the dawn of a new era in computing. Following ENIAC, digital computers evolved rapidly, becoming smaller, faster, and more powerful. Today, digital computers are embedded in devices ranging from smartphones and laptops to smartwatches, revolutionizing daily life.
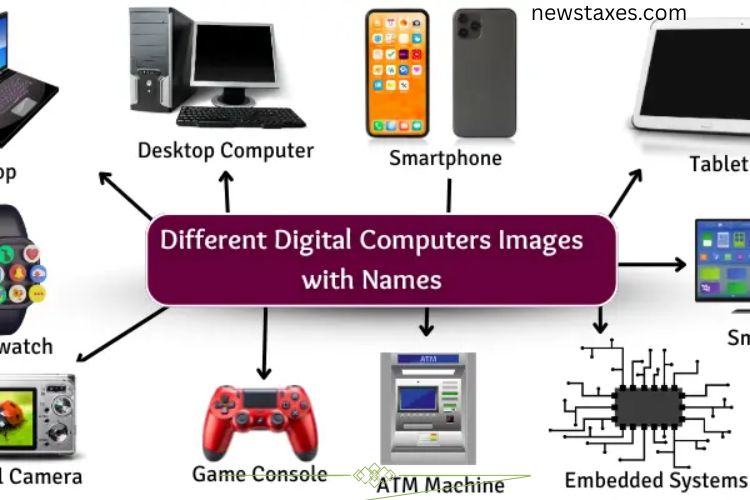
Types of Digital Computers
Digital computers are designed to serve different purposes, depending on their size, speed, and computing power. Here’s an overview of the main types:
- Microcomputers: Compact computers commonly used at home, school, or office. Examples include laptops and desktop PCs.
- Minicomputers: Medium-sized systems used by small businesses for tasks requiring more power than microcomputers.
- Mainframe Computers: Large systems capable of handling massive amounts of data, typically used by banks and corporations.
- Supercomputers: Extremely powerful machines used in scientific research, weather forecasting, and simulations.
- Workstations: High-performance computers for design, graphics, and engineering tasks.
- Embedded Computers: Integrated into machines like cars, microwaves, and industrial equipment, performing specialized functions.
Each type serves a unique purpose, enabling efficient and specialized computing for diverse applications.
Core Functions of a Digital Computer
Digital computers perform several fundamental functions that make them versatile and indispensable:
- Input: Receives data from input devices such as keyboards, mice, or scanners.
- Processing: Manipulates and analyzes data using the CPU (Central Processing Unit).
- Storage: Saves information temporarily in RAM or permanently in storage devices like hard drives or SSDs.
- Output: Delivers results through monitors, printers, or other output devices.
By performing these functions seamlessly, digital computers help individuals and organizations accomplish tasks with speed and precision.
Everyday Uses of Digital Computers
Digital computers touch nearly every aspect of daily life. Here are some key areas where they make a difference:
- Education: Students access learning resources, complete assignments, and research topics online.
- Office Work: Professionals write documents, manage emails, conduct virtual meetings, and organize data efficiently.
- Banking and Finance: Banks rely on digital systems for secure transactions, account management, and record-keeping.
- Healthcare: Doctors and hospitals use computers to track patient records, diagnose illnesses, and schedule treatments.
- Shopping: Online stores and e-commerce platforms make shopping convenient and fast.
- Communication: Email, video calls, and messaging apps enable instant global communication.
- Entertainment: Streaming movies, listening to music, and playing games are all powered by digital computing.
- Science and Research: Scientists and researchers use high-powered computers for simulations, experiments, and data analysis.
From personal use to industrial applications, digital computers improve productivity and enhance experiences across all fields.
Advantages of Digital Computers
Digital computers offer numerous benefits that have reshaped modern life:
- Speed: They process information almost instantly.
- Accuracy: Digital systems reduce human errors significantly.
- Large Storage: They can store vast amounts of data for quick access.
- Ease of Use: User-friendly interfaces make computing accessible to all.
- Multitasking: They can perform multiple tasks simultaneously without fatigue.
- Time-Saving: Digital computers automate repetitive tasks, freeing up human effort.
- Productivity Boost: Businesses and individuals achieve more in less time.
- Software Versatility: They support a wide range of applications, from work tools to entertainment.
The combination of speed, reliability, and versatility makes digital computers indispensable in both personal and professional contexts.
Limitations of Digital Computers
While digital computers bring immense benefits, they also have some drawbacks:
- Dependency on Electricity: They require power to function.
- Eye Strain: Prolonged use can affect eyesight.
- Cost: High-end computers can be expensive.
- Vulnerability to Viruses: Digital systems need protection against malware.
- Reduced Physical Activity: Extended computer use can encourage sedentary lifestyles.
- Distractions: Games, social media, and other applications can reduce focus.
- Addiction Risk: Overuse may lead to dependency.
- Maintenance Needs: Computers require regular updates and care.
- Privacy Concerns: Digital systems can compromise personal information if not secured.
Understanding these limitations helps users adopt healthy, safe, and effective computer practices.
The Future of Digital Computers
Digital computers continue to evolve at a rapid pace. Innovations such as quantum computing, artificial intelligence, and cloud computing promise to expand their capabilities beyond imagination. These technologies aim to make computers faster, smarter, and even more integrated into daily life, transforming industries like healthcare, education, finance, and entertainment.
As technology progresses, digital computers will play an even more central role in shaping society, enhancing human potential, and solving complex global challenges.
Frequently Asked Questions:
What is a digital computer?
A digital computer is a machine that processes data in the form of numbers, mainly 0s and 1s. It takes input, processes it using a CPU, stores information, and produces output for various tasks.
How is a digital computer different from an analog computer?
Unlike analog computers that use continuous signals, digital computers work with discrete numbers. This makes them faster, more accurate, and easier to store and process data.
What are the main types of digital computers?
Digital computers include microcomputers, minicomputers, mainframes, supercomputers, workstations, and embedded computers. Each type is designed for specific tasks and computing power requirements.
Where are digital computers used in daily life?
They are used in education, offices, banking, healthcare, shopping, communication, entertainment, and scientific research. Digital computers make tasks faster, accurate, and more efficient.
What are the advantages of digital computers?
They offer high speed, accuracy, large storage, multitasking ability, and user-friendly interfaces. They also enhance productivity and support a wide range of software applications.
What are the limitations of digital computers?
They require electricity, can cause eye strain, may be expensive, and are vulnerable to viruses. Overuse can reduce physical activity, cause distractions, or lead to privacy concerns.
Who invented the first digital computer?
The first digital computer, ENIAC, was created in 1946 by John Mauchly and J. Presper Eckert. It marked the beginning of modern computing.
Conclusion
Digital computers have revolutionized the way we live, work, and communicate. From the historic ENIAC to today’s powerful laptops, smartphones, and embedded devices, they combine speed, accuracy, and versatility to make everyday tasks easier and more efficient. While they come with challenges like security risks and potential overuse, their benefits—enhanced productivity, multitasking, and access to vast information—far outweigh the drawbacks. As technology advances, digital computers will continue to evolve, integrating innovations like artificial intelligence, quantum computing, and cloud systems.