A laptop is a sophisticated device made up of various parts that work together to provide a smooth computing experience. Some components are visible on the outside, while others remain hidden inside, performing critical functions. Understanding these parts not only helps you use your laptop efficiently but also makes troubleshooting easier. This guide explores both external and internal parts of a laptop in detail.
Read More: Unlocking the Incredible Power of Keyboards: Essential Uses That Boost Productivity and Creativity
External Parts of a Laptop
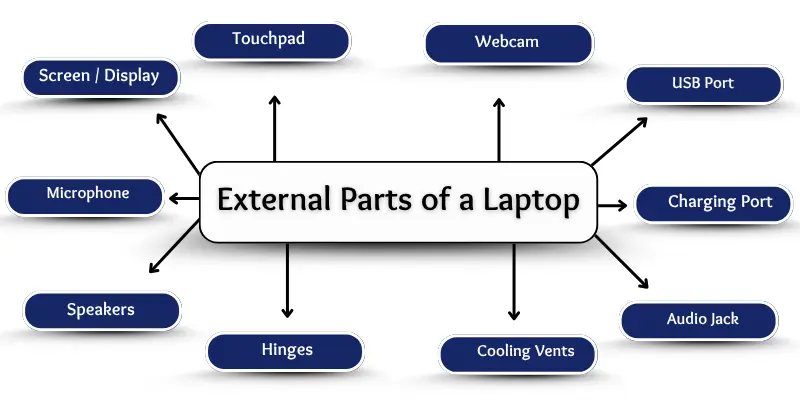
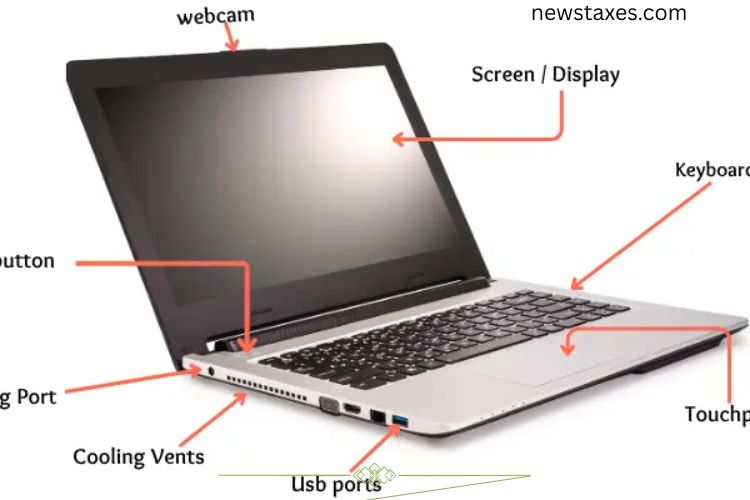
External parts are the components you can see and touch. They are designed to make interaction with your laptop easier, providing input, output, and connectivity options. Here are the key external parts:
Screen / Display
The screen is the most noticeable part of a laptop. It displays everything from text to high-definition videos, enabling you to read, watch, and work. Modern laptops use LED or LCD displays, offering clarity and vivid colors. Without the screen, you cannot see the laptop’s output, making it an essential part.
Keyboard
The keyboard allows you to type letters, numbers, and symbols. Whether you are writing emails, working on assignments, or coding, the keyboard is your primary tool to communicate commands to the laptop. Each key has a specific function, and modern keyboards often include shortcuts for increased productivity.
Touchpad (Trackpad)
The touchpad is a flat, sensitive surface usually located below the keyboard. It lets you control the cursor, click, drag, and scroll without an external mouse. Some touchpads support gestures, like two-finger scrolling or zooming, enhancing ease of navigation.
Webcam
A webcam is a small camera located at the top of the screen. It captures video and images, making it essential for video calls, online classes, and virtual meetings. Webcams have become a standard feature in laptops, enabling clear communication in professional and personal settings.
Microphone
The built-in microphone records audio for video calls, lectures, and voice commands. It captures your voice and transmits it clearly during online communication, ensuring smooth interaction in virtual environments.
Speakers
Integrated speakers provide audio output, allowing you to listen to music, watch videos, or participate in calls without external devices. While built-in speakers may not match the quality of external ones, they are sufficient for everyday tasks.
Power Button
The power button turns your laptop on and off. Typically located near the keyboard or on the side, it starts the boot process and shuts down the device safely. Without it, you cannot operate the laptop.
USB Ports
USB ports connect your laptop to peripherals such as mice, keyboards, or external storage drives. They also enable data transfer and device charging. Most laptops feature multiple USB ports, increasing connectivity options.
Charging Port
The charging port is where the power adapter connects to supply electricity to the laptop. It ensures your device stays powered and charges the battery for portable use.
Audio Jack
The audio jack allows headphones or earphones to connect directly to your laptop. It provides private listening for music, movies, and video calls, making it a simple yet essential feature.
SD Card Slot
The SD card slot enables you to transfer files such as photos, videos, or documents from cameras and smartphones to your laptop quickly. It is widely used by students, photographers, and professionals for fast file sharing.
Hinges
Hinges connect the display to the laptop’s base, allowing the screen to open and close smoothly. They maintain screen stability and ensure proper alignment while using the device.
Cooling Vents
Cooling vents prevent overheating by releasing hot air from inside the laptop. Proper ventilation ensures the device runs efficiently and extends its lifespan.
External Battery (Removable)
Some laptops feature removable batteries, which provide portable power. A weak battery can affect performance, and replacing it can extend the device’s usability.
Internal Parts of a Laptop
Internal parts are hidden within the laptop but are vital for its operation. These components handle processing, storage, connectivity, and overall performance.
Motherboard
The motherboard is the central circuit hub connecting all internal components, including the CPU, RAM, storage, and GPU. It allows communication between parts, making it the “heart” of the laptop. Without a functioning motherboard, the laptop cannot operate.
CPU (Central Processing Unit)
The CPU is the brain of the laptop. It processes instructions, runs applications, and manages tasks. Every action, from opening a file to playing a game, depends on the CPU’s performance. A powerful CPU ensures smooth multitasking and fast processing.
RAM (Random Access Memory)
RAM temporarily stores data for quick access by the CPU. It allows multiple programs to run simultaneously without slowing down the laptop. Insufficient RAM can cause delays and hinder productivity, while larger RAM improves speed and efficiency.
Hard Drive / SSD (Storage)
Storage holds your files, applications, and operating system. Traditional Hard Disk Drives (HDDs) store data magnetically, while Solid State Drives (SSDs) use flash memory for faster access. SSDs significantly improve startup time and file transfer speed, making them ideal for modern laptops.
GPU (Graphics Processing Unit)
The GPU manages visuals, rendering images, videos, and games. Laptops with strong GPUs deliver smoother graphics and better performance in gaming, video editing, and graphic-intensive tasks. While CPUs handle general processing, GPUs excel at graphics computation.
Internal Battery
An internal battery powers the laptop when unplugged. Unlike removable batteries, it is fixed inside and must be charged through the laptop’s charging port. The battery allows portable computing for extended periods.
Cooling Fan / Heat Sink
Cooling fans and heat sinks regulate temperature inside the laptop. They remove excess heat generated by the CPU and GPU, preventing damage and maintaining performance. Effective cooling ensures longevity and prevents unexpected shutdowns.
Wi-Fi Card
The Wi-Fi card connects the laptop to wireless networks. It detects signals and enables internet access without cables, supporting browsing, streaming, and online communication.
Bluetooth Module
The Bluetooth module enables wireless connectivity with other devices like headphones, keyboards, mice, and smartphones. It facilitates easy file sharing and device pairing, enhancing convenience.
CMOS Battery
The CMOS battery powers the BIOS memory, which stores system settings like date, time, and hardware configuration. Even when the laptop is turned off, the CMOS battery preserves these essential settings.
Internal Speakers
Internal speakers are small audio components built into the laptop. They provide sound output for media playback, notifications, and video calls, eliminating the need for external audio devices in everyday use.
Frequently Asked Questions:
What are the main external parts of a laptop?
The main external parts include the screen, keyboard, touchpad, webcam, microphone, speakers, power button, USB ports, charging port, audio jack, SD card slot, hinges, cooling vents, and, in some laptops, a removable battery.
What is the function of the laptop screen?
The screen displays text, images, videos, and applications. It is your primary visual interface for interacting with the laptop.
How does the keyboard help in laptop usage?
The keyboard allows you to input text, numbers, and commands. It is essential for typing, programming, and navigating software.
What is the role of the touchpad?
The touchpad controls the cursor, allowing you to click, drag, scroll, and perform gestures without using an external mouse.
Why is the CPU called the brain of the laptop?
The CPU (Central Processing Unit) processes all instructions, runs programs, and manages the laptop’s operations, making it the core of computing performance.
How does RAM affect laptop performance?
RAM (Random Access Memory) temporarily stores data for fast access by the CPU. More RAM enables smoother multitasking and faster performance.
What is the difference between HDD and SSD storage?
HDDs store data mechanically and are slower, while SSDs use flash memory for faster startup, file access, and overall improved laptop speed.
Conclusion
Laptops are intricate devices made up of both visible external components and hidden internal parts, each playing a crucial role in performance, usability, and durability. External parts like the screen, keyboard, touchpad, and ports make interaction seamless, while internal components such as the CPU, RAM, storage, and GPU ensure fast processing, smooth multitasking, and stunning visuals. Understanding these essential laptop components empowers users to make informed decisions when buying, maintaining, or upgrading their devices. By knowing how each part works and how they connect, you can maximize your laptop’s efficiency, longevity, and overall computing experience.